
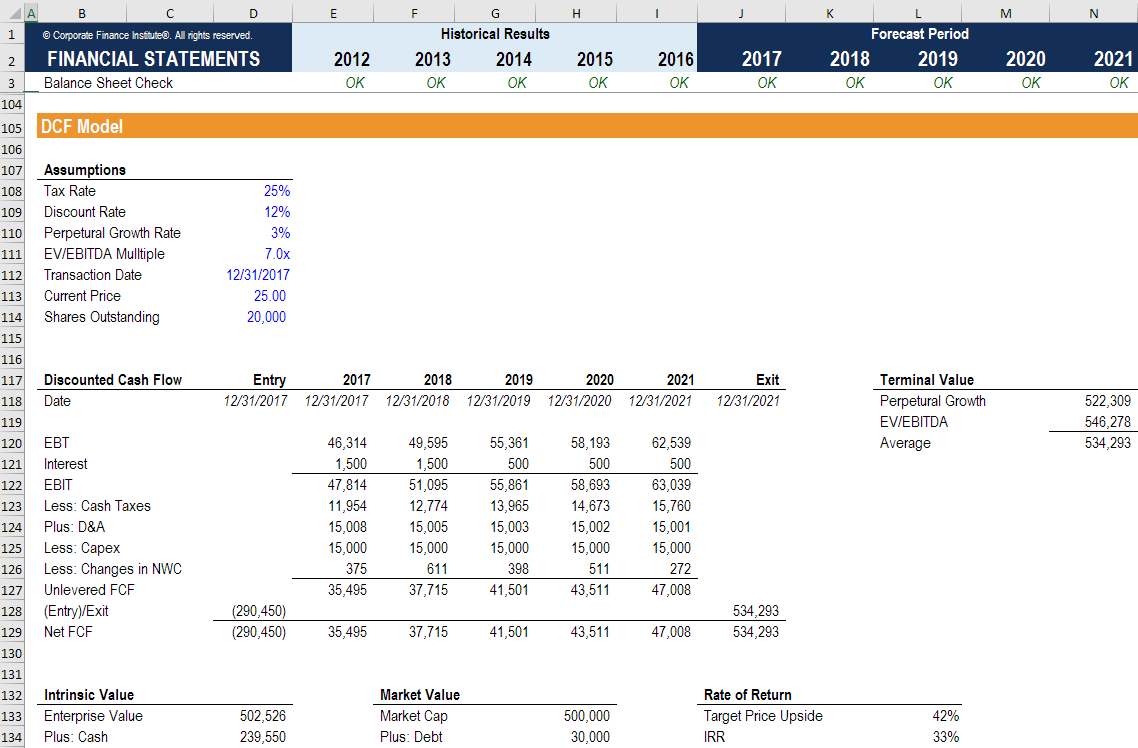
Lenders can gauge the quality of cash flow available with a company by deducting debt payments from FCFF.
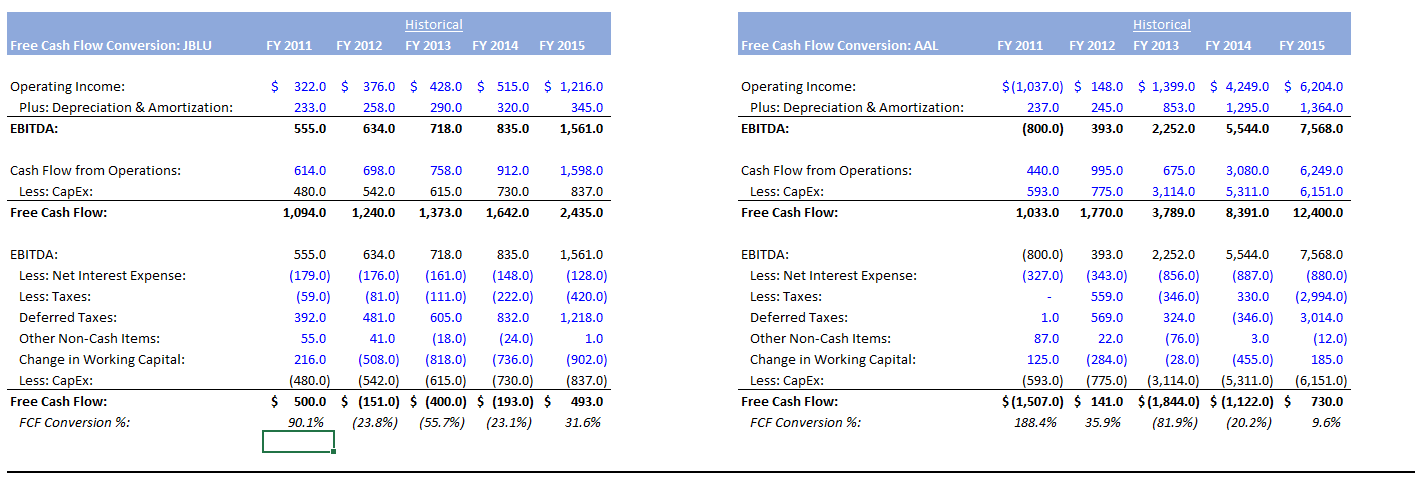
But the FCF may show a declining trend for the last three years as vendors demand faster payments, customers delay payments, or inventories rise.įCF informs lenders and shareholders whether the company can pay expected dividends and interest.

Therefore, FCF provides insight into items missing from the income statement by including working capital to measure profitability.įor example, a company witnesses a stable net income of $30,000,000 for the past ten years. Similarly, a rise in inventory levels indicates low sales. A reduction in accounts receivable shows that cash from customers is coming in quickly. A decrease in accounts payable indicates that vendors are collecting payments faster. As discussed earlier, FCF accounts for changes in the company’s working capital.
#FREE CASH FLOW FORMULA EBIT FREE#
Free Cash Flow BenefitsįCF provides insight into company value and fundamental trends. It also reduces earnings per share and negatively impacts share prices. Dilution refers to the diminishing equity positions of shareholders when the company creates or issues new shares. Analysts use FCFE to determine the value of a company and use it as an alternative to the dividend discount model, especially when a company does not pay a dividend.Īnalysts also evaluate the effect of dilution by calculating the FCF on a per-share basis. It includes capital expenditures, net income, debt, and working capital. A negative FCFF shows that the company did not generate enough revenue to pay for its expenses and investments.įree cash flow to equity (FCFE) measures equity capital usage that shows the cash available to the company’s shareholders after paying all expenses, reinvestment, and debt. This important benchmark is used to analyze and compare a company’s financial health. The firm’s free cash flow (FCFF) measures a company’s profitability after taxes, working capital, expenses, and investments. However, it accounts for spending on assets and changes in working capital shown on the balance sheet.Īnalysts and investment bankers seeking to evaluate a company’s expected performance with different structures adjust for interest payments and debt using FCF variations like free cash flow for the firm and free cash flow to equity. It does not cover the non-cash expenses shown on the income statement or interest payments. Free Cash Flow Explainedįree cash flow (FCF) is the cash the company has after paying for operations and capital assets. It reveals any problems in the company’s fundamentals before they show up on the income statement. It shows how much money is left over for investors and calculates an accurate number for earnings, so you don’t have to guess the value of the stock.įCF is the cash available for the company to pay interest and dividends to investors and to pay creditors. It is one of the essential components of discounted cash flow analysis. Free cash flow (FCF) helps eliminate the guesswork in valuation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
